Is Your Thyroid Impacting Your Fertility?
YES! Solving thyroid problems before conceiving is more important than you think! The thyroid is a very important gland for fertility. Hormonal imbalance can act as a trigger for thyroid problems.
Let’s review how the thyroid functions and learn the different ways thyroid issues may affect your fertility.
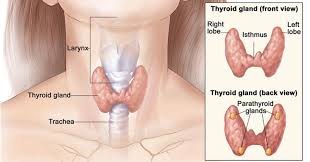
The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped gland. It is located just below the larynx, in the lower part of the neck. The purpose of the thyroid gland is to take iodine from 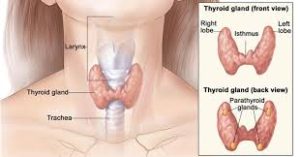 the foods we consume and convert them into thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body which can absorb iodine. The thyroid combines iodine and the amino acid tryosine to make T4 and T3. T4 and T3, once released into the blood stream control our metabolism. They thyroid is also responsible for proper growth, development and repair of the body. It is extremely important for the development of the central nervous system. The metabolism of every single cell in our body is dependent on thyroid hormones. The thyroid produces about 80% T4 and 20% T3, but T3 has four times the strength of T4.
the foods we consume and convert them into thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body which can absorb iodine. The thyroid combines iodine and the amino acid tryosine to make T4 and T3. T4 and T3, once released into the blood stream control our metabolism. They thyroid is also responsible for proper growth, development and repair of the body. It is extremely important for the development of the central nervous system. The metabolism of every single cell in our body is dependent on thyroid hormones. The thyroid produces about 80% T4 and 20% T3, but T3 has four times the strength of T4.
Our thyroid is controlled by the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is controlled by the hypothalamus. When thyroid hormones drop too low, the pituitary gland releases Thyroid Stimulation Hormone (TSH). The release of TSH stimulates th thyroid to release more T3 and T4. Healthy regulatory release of T3 and T4 signal the pituitary to decrease the release of TSH. The hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary gland to release TSH through the release of TSH Releasing Hormone (TRH). This can be so confusing. To break it down, the hypothalamus is like you – a person who can control the thermostat in your home. The thermostat is the pituitary and the heat is thyroid hormones. As the heat rises (thyroid hormones), it signals the thermostat (pituitary) to shut off. As the heat decreases, it signals the thermostat to run again. The control person (hypothalamus) sets the thrmostat (pituitary) to a regulate the heat (thyroid).
Thyroid Disease and Fertility
There are some significant symptoms associated with fertility whether you suspect a thyroid issue or know you already have a thyroid issue. If you suspect a thyroid issue, please research each pattern of disease more fully and discuss it with your doctor. Here are some symptoms in relation to fertility only. There are many other signs and symptoms associated with these thyroid diseases.
Hyperthyroidism
Overactive tissue in the thyroid gland that leads to overproduction of thyroid hormones. This is most commonly caused by inflammation of the thyroid, called thyroditis. This can be caused by a variety of reasons and may lead to Hashimoto’s thyroditis.
Fertility signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism for women
- Loss of libido
- Amenorrhea (absent period)
- Postpartum thyroditis, occurs in 7% of women within the first year after childbirth
fertility signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism for men
- Abnormal enlargement of the mammary glands in males
- Feminnization
- Loss of libido
Hypothyroidism
This happens when the thyroid is not producing enough thyroid hormones. This commonly happens when there is iodine deficiency. Hypothyroidism happens in women more often than men.
Fertility signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism for women
Early signs:
- Female infertility
- Any type of problem with the menstrual cycle
- Hyperprolactenimia (elevated prolactin hormone)
- Galactorrhea (flow of milk in the absence of pregnancy or childbirth)
Late signs:
- Abnormal menstrual cycles
- Low Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
For Men, uncommon signs that show up affecting fertility
- Decreased libido in men; creates impairment of testicular testosterone synthesis
- Abnormal enlargement of the mammary glands in males
Untreated or poorly treated hypothyroidism may cause serious complications for pregnancy, in both the mother and the baby. Because Hashimoto’s thyroditis may lead to hypothyroidism, these risks for complications fall under the thyroid problem as well.
Complications for the mother:
- Anemia (iron deficiency)
- Miscarriage
- Preeclampsia
- Placental abruption (placenta detaches from wall of uterus pre-term)
- Postpartum hemorhage
Complications for the baby:
- Preterm birth
- Low birth weight
- Thyroid problems
- Stillbirth
- Birth defects
Hashimoto’s thyroditis
This thyroid disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder. They thyroid gland is destroyed by cell and antibody immune response. As the thyroid gland is attacked, the thyroid function decreases; less and less thyroid hormones are released which leads to Hypothyroidism. Hashimoto’s main fertility symptom is infertility.
Some women experience thyroid issues after pregnancy, around 7%. 20% of those women that experience hyperthyroidism will develop Hashimoto’s thyroditis. For these women, the thyroid becomes overactive due to inflammation and then this triggers an immune response. The immune response attacks the thyroid, which eventually decreases its function and leads to hypothyroidism. Doctors still do not know why autoimmune diseases happen.
Want to know if your symptoms relate to thyroid issues? Take our quiz!
Up Next – Treating Thyroid Problems Naturally
How can we help?




[…] this to read about thyroid issues and how the thyroid […]